Employee remuneration is a fundamental aspect of the employer-employee relationship, encompassing the compensation, benefits, and deductions provided to workers for their services.
While compensation packages are designed to reward and incentivize employees, it is essential to navigate the legal and ethical boundaries that govern the deductions and prohibitions on employee remuneration. Employers must be well-versed in the applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards to ensure fair and transparent practices while safeguarding the rights and interests of their workforce.
All employees are required to pay tax as well as contribute to the social security fund or provident fund based on their earned salary. Employers too are obligated to withhold a certain amount for a tax deduction before paying the employees their salary. Additionally, the Labor Act allows for additional deductions from an employee's salary. However, there are certain circumstances where deductions are not permitted.
Deductions that are Allowed:
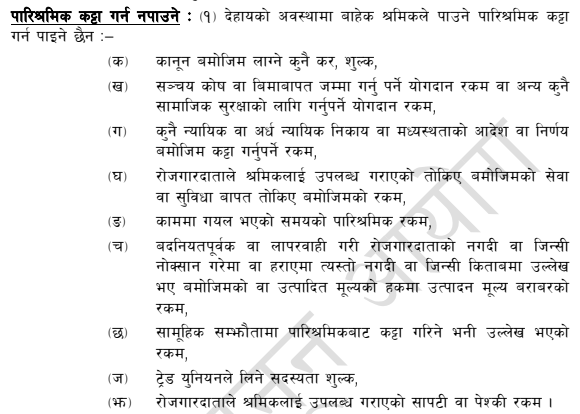
An employer is allowed to make the following deductions from an employee’s salary. Except in the following circumstance, no amount shall be deducted from the remuneration receivable by the employees:
Any tax, fees leviable under law
Contribution required for provident funds, insurance, or other social security schemes.
Deduction mandated by any judicial or quasi-judicial body or arbitration
The amount prescribed for service or facility provided by the employer to the employee
Amount of remuneration for the period during which the employee remains absent from the work
In the event of loss of or damage to cash or in-kind of the employer with ulterior motive or recklessly, such amount as mentioned in the cash or in-kind book or the amount equivalent to the production cost in the case of a manufactured good
Deductions specified in collective agreements.
Trade union membership fees.
Amount of loan or advance provided or paid to the employee by the employer.
Prohibition On Deduction Of Remuneration

The deduction shall be made from the monthly remuneration that remains after subtracting the amounts from tax and provident fund or insurance or any other social security.
Where an employee is relieved of employment services or loses one’s life before the deduction is made, in such cases whatever deduction needs to be made shall be reduced from any amount whatsoever payable to such an employee.
In the circumstance of the employee’s demise, if the deducted amount cannot be recovered, then the employer shall give notice of fifteen days to the legal heir for payment.
Where the amount remains unpaid after fifteen days, the employer may make a petition to the court for the recovery of such an amount within thirty-five days of the expiry of the period.
Remuneration deduction for reserve employee

For the reserve employees, who work on a need basis, employers will pay half the remuneration until work is resumed.
Reserve employees shall not be required to make attendance in the workplace during the reserve period unless the requirement of attendance is mentioned in the notice on holding the employee in reserve.
Overall, understanding and implementing these practices as per the Labor Act is essential for employers to maintain a fair and harmonious work environment while fulfilling their obligations towards their workers.
For more informative blog, click here.














